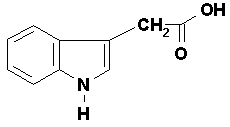
 |
| Photo and information found at http://www.plant-hormones.info/auxins.htm |
- stimulates cell elongation in stem
- stimulates cell division in cambium
- Stimulates differentiation of phloem and xylem
- Stimulates root initiation on stem cuttings and lateral root development in tissue culture
- Mediates the tropistic response of bending in response to gravity and light
- The auxin supply from the apical bud suppresses growth of lateral buds
- Delays leaf senescence
- Can inhibit or promote (via ethylene stimulation) leaf and fruit abscission
- Can induce fruit setting and growth in some plants
- Involved in assimilate movement toward auxin possibly by an effect on phloem transport
- Delays fruit ripening
- Promotes flowering in Bromeliads
- Stimulates growth of flower parts
- Promotes (via ethylene production) femaleness in dioecious flowers
 |
| Photo and information found at http://www.plant-hormones.info/abscisicacid.htm |
Abscisic Acid - single compound; functions in plant development process
- Stimulates the closure of stomata (water stress brings about an increase in ABA synthesis).
- Inhibits shoot growth but will not have as much affect on roots or may even promote growth of roots.
- Induces seeds to synthesize storage proteins.
- Inhibits the affect of gibberellins on stimulating de novo synthesis of a-amylase.
- Has some effect on induction and maintenance of dormancy
- Induces gene transcription especially for proteinase inhibitors in response to wounding which may explain an apparent role in pathogen defense.
 |
| Photo: http://biology.kenyon.edu/edwards/project/wendy/ethylene.htm Info: http://www.plant-hormones.info/ethylene.htm |
Ethylene - gaseous hormone; used in plant ripening
- Stimulates the release of dormancy.
- Stimulates shoot and root growth and differentiation (triple response)
- May have a role in adventitious root formation.
- Stimulates leaf and fruit abscission.
- Stimulates Bromiliad flower induction.
- Induction of femaleness in dioecious flowers.
- Stimulates flower opening.
- Stimulates flower and leaf senescence.
- Stimulates fruit ripening.
No comments:
Post a Comment